Modern content management systems and cheap hosting have led to an explosion of websites: every minute an amazing
571 new sites are created. Even though these systems are easier than ever to set up and use, they aren’t infallible. There are a number of issues you could have with your page that are causing you to lag behind your competitors in the search rankings without you ever knowing. Below are 7 common on-page SEO mistakes people make without even realizing it.
1. Duplicate Content
What is it?
Duplicate content means, simply,
the same content published across multiple URLs. This causes a problem for SEO because search engines have a hard time figuring out which page is the original. If you have a page with duplicate content there’s a chance Google won’t even display it in its search results.
This, of course, can be done deliberately in an attempt to manipulate search engine results. However, you could also end up showing duplicate content completely by accident because you have multiple URLs pointing to the same content. You could be showing duplicate content on you rsite because of:
- Failure to implement WWW resolve
- Trailing slashes
- The page being accessible at both http and https
- Capital letters such as www.example.com/product-page and www.example.com/Product-page
- Pages with sorting options such as time, color, size, price or other criteria
- Printer-friendly pages
How do I fix it?
There are a few ways you can deal with duplicate content on your site:
- Using the rel=”canonical” tag. You can do this by deciding which URL you want to show up in search results (making it canon) and adding it to the of the other pages with the same content. Implementation of the rel=”canonical” tag should look like:
<link href=”https://www.example.com/page-a” rel=”canonical”>. This tells the search bots clearly this page is a copy of the canonical URL so it knows which one to show in search results and where to allocate incoming link juice.
- Your other option is to use server-side 301 redirects. 301 redirects tell search engine crawlers and servers that the website has moved permanently to another URL. You can use 301 redirects to divert traffic to your preferred URLs. For example, redirecting users from URLs with uppercase letters to those with lowercase characters, or send everyone to URLs that end in a trailing slash.
- You should also set a preferred domain in Google Search Console. Once you do this Google will use that domain in the future when it follows links and indexes pages. So if you’ve set your preferred domain as http://www.example.com and someone links to your page as http://example.com, Google will follow that link to your preferred domain. It will also take your domain preference into account when displaying search results.
2. Some or all Pages Cannot be Crawled
What is it?
As we discussed above, it can be useful to block search engine crawlers from accessing certain pages on your site. When developing or redesigning a site it’s best practice to prevent robots from indexing a site and displaying pages in search results (especially when the old site is still live). This is done via the robots.txt file. But when it’s time to bring the site online, many webmasters forget to update the file so the crawlers continue to be blocked and the new pages don’t get indexed by search engines.
How do I fix it?
Check your site’s robots.txt file. What permissions have you set for the search engine bots? If you’ve blocked access to your site to all robots your robots.txt will look like this:
User-agent:*
Disallow: /
To allow the crawlers to access your entire site, use the following:
User-agent:*
Disallow:
However, you probably don’t want to let search engines access your whole site. It’s best practice to block access to some areas like temp or junk folders or file types like PowerPoint presentations. You can do this in the robots.txt file like this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /tmp/
Disallow: /junk/
Disallow: *.ppt$
You can use Google Search Console to
test your robots.txt file for syntax and logic errors. You can also use it to test URLs to make sure they can be accessed by googlebot.
What is it?
Title tags are one of the most important elements of on-page SEO so you should include your most important keywords here. Keywords in title tags give a strong clue about the content on the page and Google heavily relies on them to determine a page’s relevance to a search. Along with
meta descriptions they form your page’s search snippet that search engines display in results pages. Treat search snippets as an advertisement in the search results; write your descriptions with an enticing message and clear call to action to maximize click-through rate.
Title tags are also used by browser tabs, bookmark descriptions and by social media sites when posting links to web pages. Make your titles unique, start with the most important keyword(s) for your page and keep them 60 characters or less.
How do I fix it?
Provide a unique meta description for your homepage and inner pages. This is important since theoretically none of your web pages are the same (that would be duplicate content!). Your meta descriptions should also include your pages’ most important keywords - they will be highlighted in bold when displayed in search results. Check Google Search Console to find issues with your descriptions such as length or duplication.
Make sure each page only has one <title> element declared in the <head> section. A properly implemented title looks like this:
<title>Page Title</title>
Since titles are used by search engines to determine ranking include keywords. But do so naturally! Search engines can tell when you’re trying to manipulate them by stuffing your title tag with keywords so don’t use more than two. The following example shows a page that packed its title with keywords relating to iPhone 5 deals and wound up on the 54th page of Google’s search results.
4. Missing Google+ Publisher Tag
What is it?
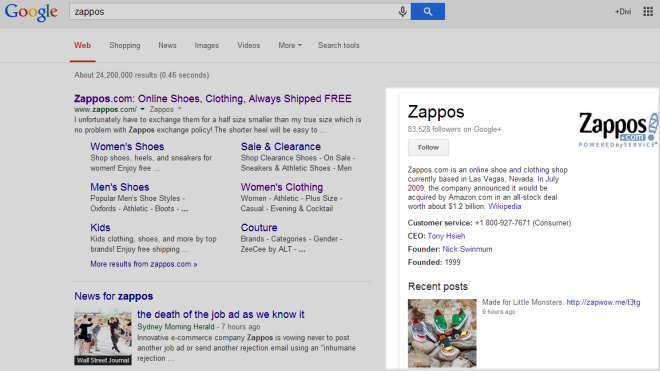
The
rel=”publisher" tag plays a key part in Google’s knowledge graph of ‘rich answers’ that appears on the right side and top of some search results pages. Knowledge graphs allow users to get more information about their searched entity without having to go to the website. The rel=”publisher” lets you link your page to your Google+ profile and provide information for Google’s knowledge graph.
Note: Google’s knowledge graph appears for branded keywords only, so a search for [zappos] will show the knowledge graph, but [zappos free shipping] won’t.
How do I fix it?
First, you need a Google+ Business page for your brand. If you don’t have one yet, go
here. You have to add your website to your Google+ page so that Google is able to connect your rich snippet to your website. Then insert the rel=”publisher” tag in the head of your site. It should look like this:
<link href=”https://plus.google.com/+yourpage” rel=”publisher” />
5. Neglecting Mobile Friendliness
What is it?
- Mobile viewport configuration
- Touchscreen readiness
- Mobile speed
Sites that neglect mobile optimization could be missing out on a significant source of traffic, particularly businesses that target local search traffic.
How do I fix it?
One of the first things you should do to improve your mobile friendliness is to set your website’s mobile viewport. The viewport is the area of a page visible to the user and varies between devices with different screen sizes. The meta viewport tag controls the page’s layout by setting the width and scale. Without a meta viewport tag mobile browsers will render a page at a desktop screen width. This can cause pages to render with an unreadable text size and tiny images. To set the mobile viewport, add the meta viewport tag in the <head> of the page like this:
<meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0”>
Setting up your mobile site with touchscreens in mind is another important aspect of mobile friendliness. It’s best to make your tap targets big (48x48 pixels with at least 32 pixels of space on all sides). More important tap targets should be bigger and further apart while less important ones can be smaller and closer together. Tap targets can be a major issue for your site’s usability when they are too small or too close together and cause visitors to either miss their target or click the wrong link.
- Just like on desktop, speed is an important part of mobile search engine results. Your mobile website has to deliver content above the fold in less than one second. In fact, each second it takes to load your page could cost you 7% in sales. Since the majority of latency for mobile users is caused by their networks, address speed tips to reduce CPU consumption first.
6. Messy URLs
What is it?
URLs are important for both SEO and human usability. Ideally, they tell robots and people how relevant the page is to a search engine query (you should still avoid stuffing your URLs with keywords!).
Keeping your URLs free of unnecessary parameters and query strings makes it easier for people to share online. It also makes it easier for search engine crawlers to determine the relevance of page content and choose what to display in results pages. URL parameters are variables in a web address that appear after the question mark (?). They can be session IDs, referral IDs or tracking codes. They can also be generated by your site’s CMS in response to dynamic page elements like filters or sorting.
How do I fix it?
The best solution to URL parameters and query strings is to rewrite your URLs. If you have an advanced CMS, such as WordPress, you can change the permalink settings in the main menu in the admin area.
Another option is to use something known as the “mod_rewrite” module available on the Apache server. When you have mod_rewrite enabled you can rewrite your URLs to make them clean with .htaccess. To do this follow these steps:
- Create a new NotePad document and save it as .htaccess.
- Paste in “RewriteEngine On”
- Add in the query string as the ReWrite Cond. For example, if your URL is
https://www.example.com/index.php?page=$1, the query string is index.php?page=$1. This tells the server that when it sees this query string it will need to rewrite the URL.
- Create the ReWrite rule in the .htaccess file like this: RewriteRule ^([a-zA-Z0-9]+)/$ index.php?page=$1 where the ^ represents the URL where the .htaccess file is stored. The ([a-zA-Z0-9]+) enables characters that are lower and uppercase letters and numbers. The + says that any number of characters is allowed. The $ sets the end of the cleaned URL.
- Load the .htaccess file into your web directory.
Learn more about ReWrite rules
here.
7. No Default 404 Error Page
What is it?
404 error pages are displayed when a page can’t be found on the server. This could happen for a variety of reasons, most of them out of your control:
- Page requested does not exist
- Server downtime
- Broken link or an incorrect URL
- The page has moved to a different URL and there is no redirect
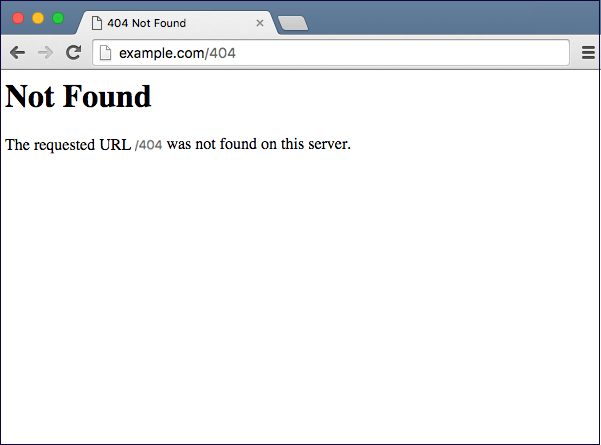
If you don’t create a 404 page for your site, the browser will show a generic error message. You can see a common default 404 page below.
The problem with generic 404 pages is that they don’t give users any links away from the page or tell them where to go next. Disrupting your users’ visits is bad enough. Stranding them on a 404 page could cost you in the future.
How do I fix it?
How you set up a custom 404 page depends on how your site was created. If it was hand coded you’ll need your website’s designer or developer to create your custom page. However, if your site was built using a CMS (content management system) it’s likely you can create your own error page. You can find documentation demonstrating how to create custom 404 pages for
Wordpress, Joomla and
Drupal.
Find some examples of great custom 404 error pages and tips on building your own
here. Once you’ve created your custom page, make sure it returns the
404 HTTP error code.
Summing it all up
You can have the best content, highest quality backlinks and extensive keyword research, but still unknowingly be hurting your rankings in search results. To avoid making these seven on-page SEO mistakes it’s important that you take your search strategy into account at the very beginning when building your website. Fortunately, we’ve outlined some of the most common on-page mistakes people make above so you can be on the lookout to fix these problems on your own page, or avoid them outright, so you can climb the search rankings and grow your traffic.
What are the most common on-page SEO mistakes you often see? Have you ever made an on-page mistake in the past without realizing it? What did you learn from it?
 . Search engines pay attention to any site that is consistently bringing in traffic. If your company’s social media pages are correctly linked back to your site, this will bring your search engine rankings up. This brings more traffic to your website which beings more traffic to your social media pages and so on.
. Search engines pay attention to any site that is consistently bringing in traffic. If your company’s social media pages are correctly linked back to your site, this will bring your search engine rankings up. This brings more traffic to your website which beings more traffic to your social media pages and so on.